Introduction to Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the study and use of structures between 1 nanometer and 100 nanometers in size. To give you an idea of how small that is, it would take eight hundred 100 nanometer particles side by side to match the width of a human hair.
With 15,342 atoms, this parallel-shaft speed reducer gear is one of the largest nanomechanical devices ever modelled in atomic detail.
Introduction to Nanotechnology: Looking At Nanoparticles
Scientists have been studying and working with
nanoparticles for centuries, but the effectiveness of their work has been
hampered by their inability to see the structure of nanoparticles. In recent
decades the development of microscopes capable of displaying particles as small
as atoms have allowed scientists to see what they are working with.
The following illustration, titled “The Scale of
Things”, created by the U. S. Department of Energy, compares
various objects to help you begin to envision precisely how small a nanometer is.
The chart starts with
objects that can be seen by the unaided eye, such as an ant, at the top and progresses to things about a nanometer or less in size, such as the
ATP molecule used in humans to store energy from food. 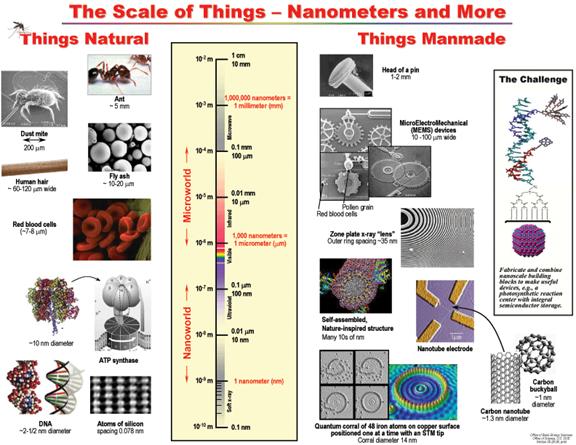

Now that you have an idea of how small-scale nanotechnologists work, consider the challenge they face. Think about how difficult it is
for many of us to insert the thread through the eye of a needle. Such an
image helps you imagine the problem scientists have working with
nanoparticles that can be as much as one-millionth the size of the
thread. Only through the use of powerful microscopes can they hope to
‘see’ and manipulate these nano-sized particles.
Introduction to Nanotechnology Applications
The ability to see nano-sized materials has opened up a world of
possibilities in a variety of industries and scientific endeavours.
Because nanotechnology is essentially a set of techniques that allow
manipulation of properties at a very small scale, it can have many
applications, such as the ones listed below.
Drug delivery.
Today, the most harmful side effects of treatments such as chemotherapy are
a result of drug delivery methods that don't pinpoint their intended
target cells accurately.
Researchers at Harvard and MIT have been able to attach special RNA
strands, measuring about 10 nm in diameter, to nanoparticles and fill
the nanoparticles with a chemotherapy drug. These RNA strands are
attracted to cancer cells. When the nanoparticle encounters a cancer
cell it adheres to it and releases the drug into the cancer cell. This
directed method of drug delivery has great potential for treating cancer
patients while producing fewer side harmful effects than those produced
by conventional chemotherapy. Fabrics.
The properties of familiar materials are being changed by manufacturers
who are adding nano-sized components to conventional materials to
improve performance. For example, some clothing manufacturers make
water and stain repellent clothing using
nano-sized whiskers in the fabric that cause water to bead up on the
surface.
Reactivity of
Materials.
The properties of many conventional materials change when formed as nano-sized
particles (nanoparticles). This is generally because nanoparticles have
a greater surface area per weight than larger particles; they are
therefore more reactive to some other molecules. For example, studies
have shown that
nanoparticles
of iron can be effective in the cleanup of chemicals in groundwater
because they react more efficiently to those chemicals than larger iron
particles.
Strength of Materials.
Nano-sized carbon particles (for example, nanotubes and buckyballs)
are extremely strong. Nanotubes and buckyballs are composed of only
carbon, and their strength comes from the special characteristics of the
bonds between carbon atoms. One proposed application that illustrates
the strength of nanosized particles of carbon is the manufacture of
t-shirt-weight
bulletproof
vests made out of carbon nanotubes.
Micro/Nano Electromechanical Systems.
The ability to create gears, mirrors, sensor elements, as well as
electronic circuitry in silicon surfaces allows the manufacture of
miniature sensors such as those used to
activate the airbags in your car. This technique is called MEMS
(Micro-electromechanical Systems). The MEMS technique results in close
integration of the mechanical mechanism with the necessary electronic
circuit on a single silicon chip, similar to the method used to produce
computer chips. Using MEMS to produce a device reduces both the cost and
size of the product, compared to similar devices made with conventional
methods. MEMS is a stepping stone to NEMS or Nano-ElectroMechanical
Systems. NEMS products are being made by a few companies and will take
over as the standard once manufacturers make the investment in the
equipment needed to produce nano-sized features.
Molecular Manufacturing.
If you're a Star Trek fan, you remember the replicator, a device that
could produce anything from a space-age guitar to a cup of Earl Grey
tea. Your favourite character just programmed the replicator, and
whatever he or she wanted appeared. Researchers are working on
developing a method called molecular
manufacturing that may someday make the Star Trek replicator a
reality. The gadget these folks envision is called a molecular
fabricator; this device would use tiny manipulators to position atoms
and molecules to build an object as complex as a desktop computer.
Researchers believe that raw materials can be used to reproduce almost
any inanimate object using this method.
The Nanotechnology Debate
There are many different points of view about nanotechnology. These
differences start with the definition of nanotechnology. Some define it
as any activity that involves manipulating materials between one
nanometer and 100 nanometers. However the original meaning of
nanotechnology involved building machines at the molecular scale and consists of the manipulation of materials on an atomic (about two-tenths of
a nanometer) scale.
The debate continues with varying opinions about exactly what
nanotechnology can achieve. Some researchers believe nanotechnology can
be used to significantly extend the human lifespan or produce replicator-like
devices that can create almost anything from simple raw materials.
Others see nanotechnology only as a tool to help us do what we do now,
but faster or better.The third major area of debate concerns the timeframe of
nanotechnology-related advances. Will nanotechnology have a significant
impact on our day-to-day lives in a decade or two, or will many of these
promised advances take considerably longer to become realities?
Finally, all the opinions about what nanotechnology can help us achieve
echo with ethical challenges. If nanotechnology helps us to increase our
lifespans or produce manufactured goods from inexpensive raw materials,
what is the moral imperative about making such technology available to
all? Is there sufficient understanding or regulation of nanotech based
materials to minimize possible harm to us or our environment?
Only time will
tell how nanotechnology will affect our lives, but browsing through the
topics on the navigation bar to the left or on our
Nanotechnology Applications
page will help you understand the possibilities and anticipate the
future.
A basic definition: Nanotechnology is the engineering of
functional systems at the molecular scale. This covers both current work and
concepts that are more advanced.
In its original sense,
'nanotechnology' refers to the
projected ability to construct items from the bottom up, using techniques
and tools being developed today to make complete, high performance products.
The Meaning of Nanotechnology
When
K. Eric Drexler (right) popularized the word 'nanotechnology' in the 1980's,
he was talking about building machines on the scale of molecules, a few
nanometers
wide—motors, robot arms, and even whole computers, far smaller than a
cell. Drexler spent the next ten years describing and analyzing these incredible
devices and responding to accusations of science fiction. Meanwhile, mundane
technology was developing the ability to build simple structures on a molecular
scale. As nanotechnology became an accepted concept, the meaning of the word
shifted to encompass the simpler kinds of nanometer-scale technology. The
U.S.
National Nanotechnology Initiative was created to fund this kind of nanotech:
their definition includes anything smaller than 100 nanometers with novel
properties.
Much of the work being done today that carries the name 'nanotechnology' is not
nanotechnology in the original meaning of the word. In its traditional sense, Nanotechnology means building things from the bottom up, with atomic
precision. The renowned physicist Richard Feynman envisioned this theoretical capability as early as 1959.
I want to build a billion tiny factories, models of each other, which are manufacturing simultaneously. . . The principles of physics, as far as I can see, do not speak against the possibility of maneuvering things atom by atom. It is not an attempt to violate any laws; it is something, in principle, that can be done; but in practice, it has not been done because we are too big. — Richard Feynman, Nobel Prize winner in physics
Based on Feynman's vision of miniature factories using nanomachines to build
complex products, advanced nanotechnology (sometimes referred to as
molecular manufacturing)
will make use of positionally-controlled
mechanochemistry guided by molecular machine systems. Formulating a roadmap for development
of this kind of nanotechnology is now an
objective of a broadly based
technology roadmap project led by
Battelle (the manager of several U.S.
National Laboratories) and the
Foresight Nanotech Institute.
Shortly after this envisioned molecular machinery is created, it will result in
a
manufacturing revolution,
probably causing severe disruption. It also has serious economic, social, environmental, and military
implications.
Four Generations
Mihail (Mike) Roco of the U.S. National Nanotechnology Initiative has
described
four generations of nanotechnology development (see chart below). The
current era, as Roco depicts it, is that of passive nanostructures, materials
designed to perform one task. The second phase, which we are just entering,
introduces active nanostructures for multitasking; for example, actuators, drug
delivery devices, and sensors. The third generation is expected to begin
emerging around 2010 and will feature nanosystems with thousands of interacting
components. A few years after that, the first integrated nanosystems,
functioning (according to Roco) much like a mammalian cell with hierarchical
systems within systems, are expected to be developed.
Some experts may still insist that nanotechnology can refer to measurement or
visualization at the scale of 1-100 nanometers, but a consensus seems to be
forming around
the idea (put forward by the NNI's Mike Roco) that control and
restructuring of matter at the nanoscale is a necessary element. CRN's
definition is a bit more precise than that, but as work progresses through the
four generations of nanotechnology leading up to molecular nanosystems, which
will include molecular manufacturing,
we think it will become increasingly obvious that "engineering of functional
systems at the molecular scale" is what nanotech is really all about.
Conflicting Definitions
Unfortunately, conflicting definitions of nanotechnology and blurry
distinctions between significantly different fields have complicated the
effort to understand the differences and develop sensible, effective policy.
The risks of today's nanoscale technologies (nanoparticle toxicity, etc.)
cannot be treated the same as the risks of longer-term
molecular manufacturing (economic disruption, unstable arms race, etc.). It is a
mistake to put them together in one basket for policy consideration—each is
important to address, but they offer different problems and will require
different solutions. As used
today, the term nanotechnology usually refers to a broad collection of mostly
disconnected fields. Essentially, anything sufficiently small and interesting
can be called nanotechnology. Much of it is harmless. For the rest, much of the
harm is of familiar and limited quality. But as we will see, molecular
manufacturing will bring unfamiliar risks and new classes of problems.
General-Purpose Technology
Nanotechnology is sometimes referred to as a general-purpose technology. That's
because in its advanced form it will have significant impact on almost all
industries and all areas of society. It will offer better built, longer lasting,
cleaner, safer, and smarter
products for the home, for communications, for medicine, for transportation,
for agriculture, and for industry in
general.
Imagine a medical device that travels through the human body to seek out and destroy small clusters of cancerous cells before they can spread. Or a box no larger than a sugar cube that contains the entire contents of the Library of Congress. Or materials much lighter than steel that possess ten times as much strength. — U.S. National Science Foundation
Like electricity or
computers before it, nanotech will offer greatly improved efficiency in almost
every facet of life. But as a general-purpose technology, it will be dual-use,
meaning it will have many commercial uses and it also will have many military
uses—making far more powerful weapons and tools of surveillance. Thus it
represents not only wonderful
benefits for humanity,
but also grave risks.
A key understanding of nanotechnology is that it offers not just better
products, but a vastly improved manufacturing process. A computer can make
copies of data files—essentially as many copies as you want at little or no
cost. It may be only a matter of time until the building of products becomes
as cheap as the copying of files. That's the real meaning of nanotechnology, and
why it is sometimes seen as "the next industrial revolution."
My own judgment is that the nanotechnology revolution has the potential to change America on a scale equal to, if not greater than, the computer revolution. — U.S. Senator Ron Wyden (D-Ore.)
The power of
nanotechnology can be encapsulated in an apparently simple device called a
personal nanofactory that
may sit on your countertop or desktop. Packed with miniature chemical
processors, computing, and robotics, it will produce a wide-range of items
quickly, cleanly, and inexpensively, building products directly from blueprints.
Exponential
Proliferation
Nanotechnology not only
will allow making many high-quality products at very low cost, but it will allow
making new nanofactories at the same low cost and at the same rapid speed.
This unique (outside of biology, that is) ability to reproduce its own means of
production is why nanotech is said to be an exponential technology. It
represents a manufacturing system that will be able to make more manufacturing
systems—factories that can build factories—rapidly, cheaply, and cleanly. The
means of production will be able to reproduce exponentially, so in just a few
weeks a few nanofactories conceivably could become billions. It is a
revolutionary, transformative, powerful, and potentially very
dangerous—or
beneficial—technology.
How soon will all this come about? Conservative estimates usually say 20 to 30
years from now, or even much later than that. However, CRN is concerned that it
may occur
sooner, quite possibly
within the next decade. This is because of the rapid progress being made in
enabling technologies, such as optics, nanolithography, mechanochemistry and 3D
prototyping. If it does arrive that soon, we may not be adequately
prepared, and the
consequences could be severe.
We believe it's not too early to begin asking some tough
questions and facing the issues:
| |
| |
| |
|
Many of these questions
were first raised over a decade ago, and have not yet been answered. If the
questions are not answered with deliberation, answers will evolve independently
and will take us by surprise; the surprise is likely to be unpleasant.
It is difficult to say for sure how soon this technology will mature, partly
because it's possible (especially in countries that do not have open societies)
that clandestine military or industrial development programs have been going on
for years without our knowledge.
We cannot say with certainty that full-scale nanotechnology will not be
developed within the next ten years or even five years. It may take longer than
that, but prudence—and possibly our survival—demands that we
prepare now for
the earliest plausible development scenario.
Managing Magic
"Any
sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic."
—
Arthur C. Clarke
The coming technological revolution
It seems like magic. A small appliance, about the size of a washing machine,
that is able to manufacture almost anything. It is called a
nanofactory. Fed
with simple chemical stocks, this amazing machine breaks down molecules, and
then reassembles them into any product you ask for. Packed with
nanotechnology
and robotics, weighing 200 pounds and standing half as tall as a person, it can
produce two tons per day of products. Control is simple: a touch screen selects
the type and number of products to produce. It costs very little to operate,
just the price of materials fed into it. In one hour, $20 worth of chemicals can
be converted into 100 pairs of shoes, or 50 shovels, or 200 cell phones, or even
a duplicate nanofactory!
Impossible? Today, maybe, but not tomorrow. The technology to create such a
machine is speedily being developed. A nanofactory will result in a
convergence between nanotechnology (molecular scale engineering), rapid
prototyping, and automated assembly. These are all present-day technologies.
None of them has yet reached its full potential, but each of them is advancing
rapidly, driven by powerful economic, social, and military forces. The
integration of the three technologies will be far more powerful than the sum of
the parts.
Some experts claim that a crash program started today could complete the first
working nanofactory within a decade at the cost of between five and
ten billion dollars. And once the first one is built, it can start making copies
of itself. Of course, five to ten billion dollars is a lot of money, and many
people will question if it could not be better spent on something else. But
imagine the economic, environmental and humanitarian benefits, when nearly any
product can be manufactured on the spot for about $1 per pound. No more shipping
costs or time spent waiting. No more wasted resources or hazardous byproducts.
No more starvation, homelessness, or poverty.
Already scientists have made chemical reactions happen by directly manipulating
the individual atoms. They can draw lines of chemicals only ten atoms wide. They
can send electricity down molecular wires. They can attach propellers to
molecular motors and analyze their performance. They can make functioning
tweezers from DNA molecules. Within a few years, we will have the ability to
build three-dimensional, active, molecular constructions. It's a small and
predictable step to building robots and chemical plants at the
nanometer scale.
It sounds too good to be true: a non-polluting, personal-size machine that
within a few hours and for a few dollars can manufacture almost
anything—clothing, books, tools, communication devices—but there is a catch. It
can also manufacture weapons, poisons, tiny surveillance cameras, and other
illicit products. How will this be controlled?
Imagine the
possibilities! And the problems...
What we're doing about it
The mission of the Center for Responsible Nanotechnology
(a non-profit program of
World Care) is to raise awareness
of the issues presented by
molecular nanotechnology: the
benefits and
dangers,
and the possibilities for responsible use.
Designing and developing molecular nanotechnology (MNT) is a major challenge in itself. It
will not be easy, and it will not happen overnight. But it will happen, and it
should happen. A greater challenge—and one that has not been addressed—is
creating the infrastructure to administer the most powerful technology
imaginable in a way that allows its safe and effective use, but that
protects investors, users, and innocent bystanders.
"Nanotechnology will give rise to a host of novel social, ethical, philosophical and legal issues. It will be important to have a group in place to predict and work to alleviate anticipated problems."— US Rep. Mike Honda (D-Cal.)
The technology is already on its way. But who will control it? If
MNT is not administered properly, there is great risk of it being used
badly—either by the entity that first develops it, or by groups that later gain
access to it. Development or control of the technology by a special interest
group would probably lead to military or economic oppression. Two competing
programs could lead to an unstable arms race. Uncontrolled release would make
the full power of the technology available to terrorists, criminals, dictators,
and irresponsible users. The safest course appears to be a single, rapid, worldwide
development program by an organization that recognizes the necessity of wise
administration.
Christine
Peterson of the
Foresight
Nanotech Institute made this point in her April 2003
testimony to the
US House
Committee on Science:
"In developing a powerful technology, delay may seem to add safety, but the opposite could be the case for molecular manufacturing. A targeted R&D project today aimed at this goal would need to be large and, therefore, visible and relatively easy to monitor. As time passes, the nanoscale infrastructure improves worldwide, enabling faster development everywhere, including places that are hard to monitor. The safest course may be to create a fast-moving, well-funded, highly-focused project located where it can be closely watched by all interested parties. Estimates are that such a project could reach its goal in 10-15 years."
CRN is dedicated to studying the problem of how to make MNT as safe
as possible. We will find technological solutions and plan systems of
administration. We will work to educate people at all levels about the dangers
of nanotechnology, and the possible solutions to those dangers.
Beyond addressing measures of safety and environmental protection, we believe
that responsible use of MNT should include consideration for ways to
reduce the gap between the haves and the have-nots. This new technology can make
a tremendous impact for good; unwise regulation might impede such hopes. As
suggested in the
Foresight Guidelines: "Experimenters and industry should have the maximum
safe opportunities to develop and commercialize the molecular manufacturing
industry. In addition, MNT should be developed in
ways that make it possible to distribute the benefits of the technology to the
four-fifths of humanity currently desperate to achieve material wealth at any
environmental or security cost."
Effective administration will not be easy, and it is unlikely that a wise course
of action can evolve without guidance. There are too many risks to avoid, too
many benefits to preserve, and too many special interests to satisfy. A
technology this powerful has implications in the areas of national security,
commercial rights, human rights, global environment, and even cultural
stability. Any single organization with a narrow focus will create too many
regulations while trying to control things that it does not know how to control;
too many regulations will create an unregulated black market, which creates
unacceptable risks. We believe that MNT must be regulated at a global
level, but the regulatory system must be designed with extreme care to be
acceptable to the world's population—and to avoid the internal corruption that
naturally accompanies so much power. The design of such a system is one of our
main concerns.
Simple, non-factory forms of nanotechnology already are being developed, and already
are raising safety questions. Although these simple forms are less
dangerous—and less useful—than the advanced nanotechnology that is our main
concern, we will be addressing today's issues of safety as well as tomorrow's.
The purpose of CRN is to investigate the wise use of molecular nanotechnology, and to
educate those who will influence its use, or be affected by it. Through this we
hope to see our vision made real: a world in which MNT is widely used
for productive and beneficial purposes, and where malicious uses are limited by
effective administration of the technology.
Exploring the Molecular World
In a scenario in the last chapter,
we saw Joel Gregory manipulating molecules in the virtual reality of a simulated
world using video goggles, tactile gloves, and a supercomputer. The early
twenty-first century should be able to do even better. Imagine, then, that today
you were to take a really long nap, oversleep, and wake up decades later in a
nanotechnological world.
In the twenty-first century, even more than in the twentieth, it's easy to make things work without understanding them, but to a newcomer much of the technology seems like magic, which is dissatisfying. After a few days, you want to understand what nanotechnology is, on a gut level. Back in the late twentieth century, most teaching used dry words and simple pictures, but now—for a topic like this—it's easier to explore a simulated world. And so you decide to explore a simulation of the molecular world.Looking through the brochure, you read many tedious facts about the simulation: how accurate it is in describing sizes, forces, motions, and the like; how similar it is to working tools used by both engineering students and professionals; how you can buy one for your very own home, and so forth. It explains how you can tour the human body, see state-of-the-art nanotechnology in action, climb a bacterium, etc. For starters, you decide to take an introductory tour: simulations of real twentieth-century objects alongside quaint twentieth-century concepts of nanotechnology.After paying a small fee and memorizing a few key phrases (any variation of "Get me out of here!" will do the most important job), you pull on a powersuit, pocket a Talking Tourguide, step into the simulation chamber, and strap the video goggles over your eyes. Looking through the goggles, you seem to be in a room with a table you know isn't really there and walls that seem too far away to fit in the simulation chamber. But trickery with a treadmill floor makes the walk to the walls seem far enough, and when you walk back and thump the table, it feels solid because the powersuit stops your hand sharply at just the right place. You can even feel the texture of the carvings on the table leg, because the suit's gloves press against your fingertips in the right patterns as you move.
Vision and Motion
You feel as though you're falling toward the chip's surface, shrinking rapidly. In a moment, it looks roughly like Figure 1B, with your thumb still there holding it. The world grows blurrier, then everything seems to go wrong as you approach the molecular level. First, your vision blurs to uselessness—there is light, but it becomes a featureless fog. Your skin is tickled by small impacts, then battered by what feel like hard-thrown marbles. Your arms and legs feel as though they are caught in turbulence, pulling to and fro, harder and harder. The ground hits your feet, you stumble and stick to the ground like a fly on flypaper, battered so hard that it almost hurts. You asked for realism, and only the built-in safety limits in the suit keep the simulated thermal motions of air molecules and of your own arms from beating you senseless."Stop!" gives you a rest from the suit's yanking and thumping, and "Standard settings!" makes the world around you become more reasonable. The simulation changes, introducing the standard cheats. Your simulated eyes are now smaller than a light wave, making focus impossible, but the goggles snap your vision into sharpness and show the atoms around you as small spheres. (Real nanomachines are as blind as you were a moment ago, and can't cheat.) You are on the surface of the 1990s computer chip, between a cell and two blocky nanocomputers like the ones in Figure 1D. Your simulated body is 50 nanometers tall, about 1/40,000,000 your real size, and the smaller nanocomputer is twice your height. At that size, you can "see" atoms and molecules, as in Figure 1E.The simulation keeps bombarding you with air molecules, but the standard settings leave out the sensation of being pelted with marbles. A moment ago you were stuck tight to the ground by molecular stickiness, but the standard settings give your muscles the effective strength of steel—at least in simulation—by making everything around you much softer and weaker. The tourguide says that the only unreal features of the simulation have to do with you—not just your ability to see and to ignore thermal shaking and bombardment, but also your sheer existence at a size too small for anything so complex as a human being. It also explains why you can see things move, something about slowing down everything around you by a factor of 10 for every factor of 10 enlargement, and by another factor to allow for your being made stronger and hence faster. And so, with your greater strength and some adjustments to make your arms, legs, and torso less sticky, you can stand, see, feel, and take stock of the situation.
Molecular Texture
The ground underfoot, like everything around you, is pebbly with atom-sized bumps the size of your fingertips. Objects look like bunches of transparent grapes or fused marbles in a variety of pretty but imaginary colors. The simulation displays a view of atoms and molecules much like those used by chemists in the 1980s, but with a sharper 3-D image and a better way to move them and to feel the forces they exert. Actually, the whole simulation setup is nothing but an improved version of systems built in the late 1980s—the computer is faster, but it is calculating the same things. The video goggles are better and the whole-body powersuit is a major change, but even in the 1980s there were 3-D displays for molecules and crude devices that gave a sense of touching them.The gloves on this suit give the sensation of touching whatever the computer simulates. When you run a fingertip over the side of the smaller nanocomputer, it feels odd, hard to describe. It is as if the surface were magnetic—it pulls on your fingertip if you move close enough. But the result isn't a sharp click of contact, because the surface isn't hard like a magnet, but strangely soft. Touching the surface is like touching a film of fog that grades smoothly into foam rubber, then hard rubber, then steel, all within the thickness of a sheet of corrugated cardboard. Moving sideways, your fingertip feels no texture, no friction, just smooth bumps more slippery than oil, and a tendency to get pulled into hollows. Pulling free of the surface takes a firm tug. The simulation makes your atom-sized fingertips feel the same forces that an atom would. It is strange how slippery the surface is—and it can't have been lubricated, since even a single oil molecule would be a lump the size of your thumb. This slipperiness makes it obvious how nano-scale bearings can work, how the parts of molecular machines can slide smoothly.But on top of this, there is a tingling feeling in your fingers, like the sensation of touching a working loudspeaker. When you put your ear against the wall of the nanocomputer, you flinch back: for a moment, you heard a sound like the hiss of a twentieth—century television tuned to a channel with no broadcast, with nothing but snow and static—but loud, painfully loud. All the atoms in the surface are vibrating at high frequencies, too fast to see. This is thermal vibration, and it's obvious why it's also called thermal noise.
Gas and Liquid
Individual molecules still move too quickly to see. So, to add one more cheat to the simulation, you issue the command "Whoa!", and everything around seems to slow down by a factor of ten.On the surface, you now can see thermal vibrations that had been too quick to follow. All around, air molecules become easier to watch. They whiz about as thick as raindrops in a storm, but they are the size of marbles and bounce in all directions. They're also sticky in a magnet-like way, and some are skidding around on the wall of the nanocomputer. When you grab one, it slips away. Most are like two fused spheres, but you spot one that is perfectly round—it is an argon atom, and these are fairly rare. With a firm grip on all sides to keep it from shooting away like a watermelon seed, you pinch it between your steel-strong fingers. It compresses by about 10 percent before the resistance is more than you can overcome. It springs back perfectly and instantly when you relax, then bounces free of your grip. Atoms have an unfamiliar perfection about them, resilient and unchanging, and they surround you in thick swarms.At the base of the wall is a churning blob that can only be a droplet of water. Scooping up a handful for a closer look yields a swarm of molecules, hundreds, all tumbling and bumbling over one another, but clinging in a coherent mass. As you watch, though, one breaks free of the liquid and flies off into the freer chaos of the surrounding air: the water is evaporating. Some slide up your arm and lodge in the armpit, but eventually skitter away. Getting rid of all the water molecules takes too much scraping, so you command "Clean me!" to dry off.
Too Small and Too Large
Beside you, the smaller nanocomputer is a block twice your height, but it's easy to climb up onto it as the tourguide suggests. Gravity is less important on a small scale: even a fly can defy gravity to walk on a ceiling, and an ant can lift what would be a truck to us. At a simulated size of fifty nanometers, gravity counts for nothing. Materials keep their strength, and are just as hard to bend or break, but the weight of an object becomes negligible. Even without the strength-enhancement that lets you overcome molecular stickiness, you could lift an object with 40 million times your mass—like a person of normal size lifting a box containing a half-dozen fully loaded oil tankers. To simulate this weak gravity, the powersuit cradles your body's weight, making you feel as if you were floating. This is almost like a vacation in an orbital theme park, walking with stickyboots on walls, ceilings, and whatnot, but with no need for anti-nausea medication.On top of the nanocomputer is a stray protein molecule, like the one in Figure 1E. This looks like a cluster of grapes and is about the same size. It even feels a bit like a bunch of grapes, soft and loose. The parts don't fly free like a gas or tumble and wander like a liquid, but they do quiver like gelatin and sometimes flop or twist. It is solid enough, but the folded structure is not as strong as your steel fingers. In the 1990s, people began to build molecular machinery out of proteins, copying biology. It worked, but it's easy to see why they moved on to better materials.From a simulated pocket, you pull out a simulated magnifying glass and look at the simulated protein. This shows a pair of bonded atoms on the surface at 10 times magnification, looking like Figure 1F. The atoms are almost transparent, but even a close look doesn't reveal a nucleus inside, because it's too small to see. It would take 1,000 times magnification to be able to see it, even with the head start of being able to see atoms with your naked eye. How could people ever confuse big, plump atoms with tiny specks like nuclei? Remembering how your steel-strong fingers couldn't press more than a fraction of the way toward the nucleus of an argon atom from the air, it's clear why nuclear fusion is so difficult. In fact, the tourguide said that it would take a real-world projectile over a hundred times faster than a high-powered rifle bullet to penetrate into the atomic core and let two nuclei fuse. Try as you might, there just isn't anything you could find in the molecular world that could reach into the middle of an atom to meddle with its nucleus. You can't touch it and you can't see it, so you stop squinting though the magnifying glass. Nuclei just aren't of much interest in nanotechnology.
Puzzle Chains
Taking the advice of the tour guide, you grab two molecular knobs on the protein and pull. It resists for a moment, but then a loop comes free, letting other loops flop around more, and the whole structure seems to melt into a writhing coil. After a bit of pulling and wrestling, the protein's structure becomes obvious: It is a long chain—longer than you are tall, if you could get it straight—and each segment of the chain has one of several kinds of knobs sticking off to the side. With the multicolored, glassy-bead portrayal of atoms, the protein chain resembles a flamboyant necklace. This may be decorative, but how does it all go back together? The chain flops and twists and thrashes, and you pull and push and twist, but the original tight, solid packing is lost. There are more ways to go wrong in folding up the chain than there are in solving Rubik's Cube, and now that the folded structure is gone, it isn't even clear what the result should look like. How did those twentieth-century researchers ever solve the notorious "protein folding problem"? It's a matter of record that they started building protein objects in the late 1980s.This protein molecule won't go back together, so you try to break it. A firm grip and a powerful yank straightens a section a bit, but the chain holds together and snaps back. Though unfolding it was easy, even muscles with the strength of steel—the strength of Superman—can't break the chain itself. Chemical bonds are amazingly strong, so it's time to cheat again. When you say, "Flimsy world—one second!" while pulling, your hands easily move apart, splitting the chain in two before its strength returns to normal. You've forced a chemical change, but there must be easier ways since chemists do their work without tiny superhands. While you compare the broken ends, they thrash around and bump together. The third time this happens, the chain rejoins, as strong as before. This is like having snap-together parts, but the snaps are far stronger than welded steel. Modern assembler chemistry usually uses other approaches, but seeing this happen makes the idea of molecular assembly more understandable: Put the right pieces together in the right positions, and they snap together to make a bigger structure.Remembering the "Whoa!" command, you decide to go back to the properly scaled speed for your size and strength. Saying "Standard settings!," you see the thrashing of the protein chain speed up to hard-to-follow blur.
Nanomachines
At your feet is a ribbed, ringed cylindrical object about the size of a soup can—not a messy, loosely folded strand like the protein (before it fell apart), but a solid piece of modern nanotechnology. It's a gear like the one in Figure 1E. Picking it up, you can immediately feel how different it is from a protein. In the gear, everything is held in place by bonds as strong as those that strung together the beads of the protein chain. It can't unfold, and you'd have to cheat again to break its perfect symmetry. Like those in the wall of the nanocomputer, its solidly attached atoms vibrate only slightly. There's another gear nearby, so you fit them together and make the atomic teeth mesh, with bumps on one fitting into hollows on the other. They stick together, and the soft, slick atomic surfaces let them roll smoothly.Underfoot is the nanocomputer itself, a huge mechanism built in the same rigid style. Climbing down from it, you can see through the transparent layers of the wall to watch the inner works. An electric motor an arm-span wide spins inside, turning a crank that drives a set of oscillating rods, which in turn drive smaller rods. This doesn't look like a computer; it looks more like an engineer's fantasy from the nineteenth century. But then, it is an antique design–the tourguide said that the original proposal was a piece of exploratory engineering dating from the mid-1980s, a mechanical design that was superseded by improved electronic designs before anyone had the tools to build even a prototype. This simulation is based on a version built by a hobbyist many years later.The mechanical nanocomputer may be crude, but it does work, and it's a lot smaller and more efficient than the electronic computers of the early 1990s. It's even somewhat faster. The rods slide back and forth in a blur of motion, blocking and unblocking each other in changing patterns, weaving patterns of logic. This nanocomputer is a stripped-down model with almost no memory, useless by itself. Looking beyond it, you see the other block—the one on the left in Figure 1D—which contains a machine powerful enough to compete with most computers built in 1990. This computer is a millionth of a meter on a side, but from where you stand, it looks like a blocky building looming over ten stories tall. The tourguide says that it contains over 100 billion atoms and stores as much data as a room full of books. You can see some of the storage system inside: row upon row of racks containing spools of molecular tape somewhat like the protein chain, but with simple bumps representing the 1s and 0s of computer data.These nanocomputers seem big and crude, but the ground you're now standing on is also a computer—a single chip from 1990, roughly as powerful as the smaller, stripped-down nanocomputer at your side. As you gaze out over the chip, you get a better sense for just how crude things were a few decades ago. At your feet, on the smallest scale, the chip is an irregular mess. Although the wall of the nanocomputer is pebbly with atomic-scale bumps, the bumps are as regular as tile. The chip's surface, though, is a jumble of lumps and mounds. This pattern spreads for dozens of paces in all directions, ending in an irregular cliff marking the edge of a single transistor. Beyond, you can see other ridges and plateaus stretching off to the horizon. These form grand, regular patterns, the circuits of the computer. The horizon—the edge of the chip—is so distant that walking there from the center would (as the tourguide warns) take days. And these vast pieces of landscaping were considered twentieth-century miracles of miniaturization?
Cells and Bodies
Even back then, research in molecular biology had revealed the existence of smaller, more perfect machines such as the protein molecules in cells. A simulated human cell–put here because earlier visitors wanted to see the size comparisons—its on the chip next to the smaller nanocomputer. The tourguide points out that the simulation cheats a bit at this point, making the cell act as though it were in a watery environment instead of air. The cell dwarfs the nanocomputer, sprawling across the chip surface and rearing into the sky like a small mountain. Walking the nature trail around its edge would lead across many transistor-plateaus and take about an hour. A glance is enough to show how different it is from a nanocomputer or a gear: it looks organic, it bulges and curves like a blob of liver, but its surface is shaggy with waving molecular chains.Walking up to its edge, you can see that the membrane wrapping the cell is fluid (cell walls are for stiff things like plants), and the membrane molecules are in constant motion. On an impulse, you thrust your arm through the membrane and poke around inside. You can feel many proteins bumping and tumbling around in the cell's interior fluid, and a crisscrossing network of protein cables and beams. Somewhere inside are the molecular machines that made all these proteins, but such bits of machinery are embedded in a roiling, organic mass. When you pull your arm out, the membrane flows closed behind. The fluid, dynamic structure of the cell is largely self healing. That's what let scientists perform experimental surgery on cells with the old, crude tools of the twentieth century: They didn't need to stitch up the holes they made when they poked around inside.Even a single human cell is huge and complex. No real thinking being could be as small as you are in the simulation: A simple computer without any memory is twice your height, and the larger nanocomputer, the size of an apartment complex, is no smarter than one of the submoronic computers of 1990. Not even a bendable finger could be as small as your simulated fingers: in the simulation, your fingers are only one atom wide, leaving no room for the slimmest possible tendon, to say nothing of nerves.For a last look at the organic world, you gaze out past the horizon and see the image of your own, full-sized thumb holding the chip on which you stand. The bulge of your thumb rises ten times higher than Mount Everest. Above, filling the sky, is a face looming like the Earth seen from orbit, gazing down. It is your own face, with cheeks the size of continents. The eyes are motionless. Thinking of the tourguide's data, you remember: the simulation uses the standard mechanical scaling rules, so being 40 million times smaller has made you 40 million times faster. To let you pull free of surfaces, it increased your strength by more than a factor of 100, which increased your speed by more than a factor of 10. So one second in the ordinary world corresponds to over 400 million here in the simulation. It would take years to see that huge face in the sky complete a single eyeblink.Enough. At the command "Get me out!", the molecular world vanishes, and your feeling of weight returns as the suit goes slack. You strip off the video goggles—and hugely, slowly, blink.
The Silicon Valley Faire
The tour of the molecular world showed some
products of molecular manufacturing, but didn't show how they were made. The
technologies you remember from the old days have mostly been replaced—but how
did this happen? The Silicon Valley Faire is advertised as "An authentic theme
park capturing life, work, and play in the early Breakthrough years." Since
"work" must include manufacturing, it seems worth a visit.
A broad dome caps the park — "To fully capture the authentic sights, sounds, and smells of the era," the tour guide politely says. Inside, the clothes and hairstyles, the newspaper headlines, the bumper-to-bumper traffic, all look much as they did before your long nap. A light haze obscures the buildings on the far side of the dome, your eyes burn slightly, and the air smells truly authentic.
The Nanofabricators, Inc., plant offers the main display of early nanotechnology. As you near the building, the tour guide mentions that this is indeed the original manufacturing plant, given landmark status over twenty years ago, then made the centerpiece of the Silicon Valley Faire ten years later, when . . . With a few taps, you reset the pocket tour guide to speak up less often.
Pocket Libraries
As people file into the Nanofabricator plant, there's a moment of hushed quiet, a sense of walking into history. Nanofabricators: home of the Superchip, the first mass-market product of nanotechnology. It was the huge memory capacity of Superchips that made possible the first Pocket Library.This section of the plant now houses a series of displays, including working replicas of early products. Picking up a Pocket Library, you find that it's not only the size of a wallet, but about the same weight. Yet it has enough memory to record every volume in the Library of Congress—something like a million times the capacity of a personal computer from 1990. It opens with a flip, the two-panel screen lights up, and a world of written knowledge is at your fingertips. Impressive."Wow, can you believe these things?" says another tourist as he fingers a Pocket Library. "Hardly any video, no 3-D–just words, sound, and flat pictures. And the cost! I wouldn't have bought `em for my kids at that price!"Your tour guide quietly states the price: about what you remember for a top-of-the-line TV set from 1990. This isn't the cheap manufacturing promised by mature nanotechnology, but it seems like a pretty good price for a library. Hmm . . . how did they work out the copyrights and royalties? There's a lot more to this product than just the technology . . .
Nanofabrication
The next room displays more technology. Here in the workroom where Superchips were first made, early nanotech manufacturing is spread out on display. The whole setup is surprisingly quiet and ordinary. Back in the 1980s and 1990s, chip plants had carefully controlled clean rooms with gowns and masks on workers and visitors, special workstations, and carefully crafted air flows to keep dust away from products. This room has none of that. It's even a little grubby.In the middle of a big square table are a half-dozen steel tanks, about the size and shape of old-fashioned milk cans. Each can has a different label identifying its contents: MEMORY BLOCKS, DATA-TRANSMISSION BLOCKS, INTERFACE BLOCKS. These are the parts needed for building up the chip. Clear plastic tubes, carrying clear and tea-colored liquids, emerge from the mouths of the milk cans and drape across the table. The tubes end in fist-sized boxes mounted above shallow dishes sitting in a ring around the cans. As the different liquids drip into each dish, a beater like a kitchen mixer swirls the liquid. In each dish, nanomachines are building Superchips.A Nanofab "engineer," dressed in period clothing complete with name badge, is setting up a dish to begin building a new chip. "This," he says, holding up a blank with a pair of tweezers, "is a silicon chip like the ones made with pre-breakthrough technology. Companies here in this valley made chips like these by melting silicon, freezing it into lumps, sawing the lumps into slices, polishing the slices, and then going through a long series of chemical and photographic steps. When they were done, they had a pattern of lines and blobs of different materials on the surface. Even the smallest of these blobs contained billions of atoms, and it took several blobs working together to store a single bit of information. A chip this size, the size of your fingernail, could store only a fraction of a billion bits. Here at Nanofab, we used bare silicon chips as a base for building up Nano memory. The picture on the wall here shows the surface of a blank chip: no transistors, no memory circuits, just fine wires to connect up with the Nano memory we built on top. The Nano memory, even in the early days, stored thousands of billions of bits. And we made them like this, but a thousand at a time–" He places the chip in the dish, presses a button, and the dish begins to fill with liquid."A few years latter," he adds, "we got rid of the silicon chips entirely"—he props up a sign saying THIS CHIP BUILD BEGAN AT: 2:15 P.M., ESTIMATED COMPLETION TIME: 1:00 A.M.—" and we sped up the construction process by a factor of a thousand."The chips in the dishes all look pretty much the same except for color. The new chip looks like dull metal. The only difference you can see in the older chips, further along in the process, is a smooth rectangular patch covered by a film of darker material. An animated flowchart on the wall shows how layer upon layer of Nano memory building blocks are grabbed from solution and laid down on the surface to make that film. The tour guide explains that the energy for this process, like the energy for molecular machines within cells, comes from dissolved chemicals—from oxygen and fuel molecules. The total amount of energy needed here is trivial, because the amount of product is trivial: at the end of the process, the total thickness of Nano memory structure—the memory store for a Pocket Library—amounts to one-tenth the thickness of a sheet of paper, spread over an area smaller than a postage stamp.
Molecular Assembly
The animated flowchart showed Nano memory building blocks as big things containing about a hundred thousand atoms apiece (it takes a moment to remember that this is still submicroscopic). The build process in the dishes stacked these blocks to make the memory film on the Superchip, but how were the blocks themselves built? The hard part in this molecular-manufacturing business has got to be at the bottom of the whole process, at the stage where molecules are put together to make large, complex parts.The Silicon Valley Faire offers simulations of this molecular assembly process, and at no extra charge. From the tour guide, you learn that modern assembly processes are complex; that earlier processes—like those used by Nanofabricators, Inc.—used clever-but-obscure engineering tricks; and that the simplest, earliest concepts were never built. Why not begin at the beginning? A short walk takes you to the Museum of Antique Concepts, the first wing of the Museum of Molecular Manufacturing.A peek inside the first hall shows several people strolling around wearing loosely fitting jumpsuits with attached goggles and gloves, staring at nothing and playing mime with invisible objects. Oh well, why not join the fools' parade? Stepping through the doorway while wearing the suit is entirely different. The goggles show a normal world outside the door and a molecular world inside. Now you, too, can see and feel the exhibit that fills the hall. It's much like the earlier simulated molecular world: it shares the standard settings for size, strength, and speed. Again, atoms seem 40 million times larger, about the size of your fingertips. This simulation is a bit less thorough than the last was—you can feel simulated objects, but only with your gloved hands. Again, everything seems to be made of quivering masses of fused marbles, each an atom."Welcome," says the tour guide, "to a 1990 concept for a molecular-manufacturing plant. These exploratory engineering designs were never intended for actual use, yet they demonstrate the basics of molecular manufacturing: making parts, testing them, and assembling them."Machinery fills the hall. Overall, the sight is reminiscent of an automated factory of the 1980s or 1990s. It seems clear enough what must be going on: Big machines stand beside a conveyor belt loaded with half-finished-looking blocks of some material
A factory large enough to make over 10 million Nano computers per day would fit on the edge one of today's integrated circuits. Inset shows an assembler arm together with workpiece on a conveyor belt.Since nothing is real, the exhibit can't be damaged, so you walk up to a machine and give it a poke. It seems as solid as the wall of the Nano computer in the previous tour. Suddenly, you notice something odd: no bombarding air molecules and no droplets of water—in fact, no loose molecules anywhere. Every atom seems to be part of a mechanical system, quivering thermal vibration, but otherwise perfectly controlled. Everything here is like the Nano computer or like the tough little gear; none of it resembles the loosely coiled protein or the roiling mass of the living cell.The conveyor belt seems motionless. At regular intervals along the belt are blocks of material under construction: workpieces. The nearest block is about a hundred marble-bumps wide, so it must contain something like 100 x 100 x 100 atoms, a full million. This block looks strangely familiar, with its rods, crank, and the rest. It's a Nano computer—or rather, a block-like part of a Nano computer still under construction.Standing alongside the pieces of Nano computer on the conveyor belt, dominating the hall, is a row of huge mechanisms. Their trunks rise from the floor, as thick as old oaks. Even though they bend over, they rear overhead. "Each machine," your tour guide says, "is the arm of a general-purpose molecular assembler.One assembler arm is bent over with its tip pressed to a block on the conveyor belt. Walking closer, you see molecular assembly in action. The arm ends in a fist-sized knob with a few protruding marbles, like knuckles. Right now, two quivering marbles—atoms—are pressed into a small hollow in the block. As you watch, the two spheres shift, snapping into place in the block with a quick twitch of motion: a chemical reaction. The assembler arm just stands there, nearly motionless. The fist has lost two knuckles, and the block of Nano computer is two atoms larger.The tour guide holds forth: "This general-purpose assembler concept resembles, in essence, the factory robots of the 1980s. It is a computer-controlled mechanical arm that moves molecular tools according to a series of instructions. Each tool is like a single-shot stapler or rivet gun. It has a handle for the assembler to grab and comes loaded with a little bit of matter—a few atoms—which it attaches to the workpiece by a chemical reaction." This is like the rejoining of the protein chain in the earlier tour.
Molecular Precision
The atoms seemed to jump into place easily enough; can they jump out of place just as easily? By now the assembler arm has crept back from the surface, leaving a small gap, so you can reach in and poke at the newly added atoms. Poking and prying do no good; when you push as hard as you can (with your simulated fingers as strong as steel), the atoms don't budge by a visible amount. Strong molecular bonds hold them in place.Your pocket tourguide—which has been applying the power of a thousand 1990s supercomputers to the task of deciding when to speak up—remarks, "Molecular bonds hold things together. In strong, stable materials atoms are either bonded, or they aren't, with no possibilities in between. Assemblers work by making and breaking bonds, so each step either succeeds perfectly or fails completely. In pre-breakthrough manufacturing, parts were always made and put together with small inaccuracies. These could add up to wreck product quality. At the molecular scale, these problems vanish. Since each step is perfectly precise, little errors can't add up. The process either works, or it doesn't."But what about those definite, complete failures? Fired by scientific curiosity, you walk to the next assembler, grab the tip, and shake it. Almost nothing happens. When you shove as hard as you can, the tip moves by about one-tenth of an atomic diameter, then springs back. "Thermal vibrations can cause mistakes by causing parts to come together and form bonds in the wrong place," the tour guide remarks. "Thermal vibrations make floppy objects bend further than stiff ones, and so these assembler arms were designed to be thick and stubby to make them very stiff. Error rates can be kept to one in a trillion, and so small products can be perfectly regular and perfectly identical. Large products can be almost perfect, having just a few atoms out of place." This should mean high reliability. Oddly, most of the things you've been seeing outside have looked pretty ordinary—not slick, shiny, and perfect, but rough and homey. They must have been manufactured that way, or made by hand. Slick, shiny things must not impress anyone anymore.
Molecular Robotics
By now, the assembler arm has moved by several atom-widths. Through the translucent sides of the arm you can see that the arm is full of mechanisms: twirling shafts, gears, and large, slowly turning rings that drive the rotation and extension of joints along the trunk. The whole system is a huge, articulated robot arm. The arm is big because the smallest parts are the size of marbles, and the machinery inside that makes it move and bend has many, many parts. Inside, another mechanism is at work: The arm now ends in a hole, and you can see the old, spent molecular tool being retracted through a tube down the middle.Patience, patience. Within a few minutes, a new tool is on its way back up the tube. Eventually, it reaches the end. Shafts twirl, gears turn, and clamps lock the tool in position. Other shafts twirl, and the arm slowly leans up against the workpiece again at a new site. Finally, with a twitch of motion, more atoms jump across, and the block is again just a little bit bigger. The cycle begins again. This huge arm seems amazingly slow, but the standard simulation settings have shifted speeds by a factor of over 400 million. A few minutes of simulation time correspond to less than a millionth of a second of real time, so this stiff, sluggish arm is completing about a million operations per second.Peering down at the very base of the assembler arm, you can get a glimpse of yet more assembler-arm machinery underneath the floor: Electric motors spin, and a nanocomputer chugs away, rods pumping furiously. All these rods and gears move quickly, sliding and turning many times for every cycle of the ponderous arm. This seems inefficient; the mechanical vibrations must generate a lot of heat, so the electric motors must draw a lot of power. Having a computer control each arm is a lot more awkward now than it was in pre-breakthrough years. Back then, a robot arm was big and expensive and a computer was a cheap chip; now the computer is bigger than the arm. There must be a better way—but then, this is the Museum of Antique Concepts.
Building-Blocks into Buildings
Where do the blocks go, once the assemblers have finished with them? Following the conveyor belt past a dozen arms, you stroll to the end of the hall, turn the corner, and find yourself on a balcony overlooking a vaster hall beyond. Here, just off the conveyor belt, a block sits in a complex fixture. Its parts are moving, and an enormous arm looms over it like a construction crane. After a moment, the tour guide speaks up and confirms your suspicion: "After manufacturing, each block is tested. Large arms pick up properly made blocks. In this hall, the larger arms assemble almost a thousand blocks of various kinds to make a complete Nano computer.The grand hall has its own conveyor belt, bearing a series of partially completed Nano computers. Arrayed along this grand belt is a row of grand arms, able to swing to and fro, to reach down to lesser conveyor belts, pluck million-atom blocks from testing stations, and plug them into the grand workpieces, the Nano computers under construction. The belt runs the length of the hall, and at the end, finished Nano computers turn a corner—to a yet-grander hall beyond?After gazing at the final-assembly hall for several minutes, you notice that nothing seems to have moved. Mere patience won't do: at the rate the smaller arms moved in the hall behind you, each block must take months to complete, and the grand block-handling arms are taking full advantage of the leisure this provides. Building a computer, start to finish, might take a terribly long time. Perhaps as long as the blink of an eye.Molecular assemblers build blocks that go to block assemblers. The block assemblers build computers, which go to system assemblers, which build systems, which–at least one path from molecules to large products seems clear enough. If a car were assembled by normal-sized robots from a thousand pieces, each piece having been assembled by smaller robots from a thousand smaller pieces, and so on, down and down, then only ten levels of assembly process would separate cars from molecules. Perhaps, around a few more corners and down a few more ever-larger halls, you would see a post-breakthrough car in the making, with unrecognizable engine parts and comfortable seating being snapped together in a century-long process in a hall so vast that the Pacific Ocean would be a puddle in the corner . . .Just ten steps in size; eight, starting with blocks as big as the ones made in the hall behind you. The molecular world seems closer, viewed this way.
Molecular Processing
Stepping back into that hall, you wonder how the process begins. In every cycle of their sluggish motion, each molecular assembler gets a fresh tool through a tube from somewhere beneath the floor, and that somewhere is where the story of molecular precision begins. And so you ask, "Where do the tools come from?", and the tour guide replies, "You might want to take the elevator to your left."Stepping out of the elevator and into the basement, you see a wide hall full of small conveyor belts and pulleys; a large pipe runs down the middle. A plaque on the wall says, "Mechanochemical processing concept, circa 1990." As usual, all the motions seem rather slow, but in this hall everything that seems designed to move is visibly in motion. The general flow seems to be away from the pipe, through several steps, and then up through the ceiling toward the hall of assemblers above.After walking over to the pipe, you can see that it is nearly transparent. Inside is a seething chaos of small molecules: the wall of the pipe is the boundary between loose molecules and controlled ones, but the loose molecules are well confined. In this simulation, your fingertips are like small molecules. No matter how hard you push, there's no way to drive your finger through the wall of the pipe. Every few paces along the pipe a fitting juts out, a housing with a mechanically driven rotating thing, exposed to the liquid inside the pipe, but also exposed to a belt running over one of the pulleys, embedded in the housing. It's hard to see exactly what is happening.The tour guide speaks up, saying, "Pockets on the rotor capture single molecules from the liquid in the pipe. Each rotor pocket has a size and shape that fits just one of the several different kinds of molecule in the liquid, so the process is rather selective. Captured molecules are then pushed into the pockets on the belt that's wrapped over the pulley there, then—""Enough," you say. Fine, it singles out molecules and sticks them into this maze of machinery. Presumably, the machines can sort the molecules to make sure the right kinds go to the right places.The belts loop back and forth carrying big, knobby masses of molecules. Many of the pulleys—rollers?—press two belts together inside a housing with auxiliary rollers. While you are looking at one of these, the tour guide says, "Each knob on a belt is a mechanochemical-processing device. When two knobs on different belts are pressed together in the right way, they are designed to transfer molecular fragments from one to another by means of a mechanically forced chemical reaction. In this way, small molecules are broken down, recombined, and finally joined to molecular tools of the sort used in the assemblers in the hall above. In this device here, the rollers create a pressure equal to the pressure found halfway to the center of the Earth, speeding a reaction that –""Fine, fine," you say. Chemists in the old days managed to make amazingly complex molecules just by mixing different chemicals together in solution in the right order under the right conditions. Here, molecules can certainly be brought together in the right order, and the conditions are much better controlled. It stands to reason that this carefully designed maze of pulleys and belts can do a better job of molecule processing than a test tube full of disorganized liquid ever could. From a liquid, through a sorter, into a mill, and out as tools: this seems to be the story of molecule processing. All the belts are loops, so the machinery just goes around and around, carrying and transforming molecular parts.
Beyond Antiques
This system of belts seems terribly simple and efficient, compared to the ponderous arms driven by frantic computers in the hall above. Why stop with making simple tools? You must have muttered this, because the tour guide speaks up again and says, "The Special-Assembler Exhibit shows another early molecular-manufacturing concept that uses the principles of this molecule-processing system to build large, complex objects. If a system is building only a single product, there is no need to have computers and flexible arms move parts around. It is far more efficient to build a machine in which everything just moves on belts at a constant speed, adding small parts to larger ones and then bringing the larger ones together as you saw at the end of the hall above."This does seem like a more sensible way to churn out a lot of identical products, but it sounds like just more of the same. Gears like fused marbles, belts like coarse beadwork, drive shafts, pulleys, machines and more machines. In a few places, marbles snap into new patterns to prepare a tool or make a product. Roll, roll, chug, chug, pop, snap, then roll and chug some more.As you leave the simulation hall, you ask, "Is there anything important I've missed in this molecular manufacturing tour?"The tour guide launches into a list: "Yes—the inner workings of assembler arms, with drive shafts, worm gears, and harmonic drives; the use of Diels-Alder reactions, interfacial free-radial chain reactions, and dative-bond formation to join blocks together in the larger-scale stages of assembly; different kinds of mechanochemical processing for preparing reactive molecular tools; the use of staged-cascade methods in providing feed-molecules of the right kinds with near-perfect reliability; the differences between efficient and inefficient steps in molecular processing; the use of redundancy to ensure reliability in large systems despite sporadic damage; modern methods of building large objects from smaller blocks; modern electronic Nano computers; modern methods for—""Enough!" you say, and the tour guide falls silent as you pitch it into a recycling bin. A course in molecular manufacturing isn't what you're looking for right now; the general idea seems clear enough. It's time to take another look at the world on a more normal scale. Houses, roads, buildings, even the landscape looked different out there beyond the Faire dome—less crowded, paved, and plowed than you remember. But why? The history books (well, they're more than just books) say that molecular manufacturing made a big difference; perhaps now the changes will make more sense. Yes, it's time to leave.
As you toss your goggled, gloved jumpsuit into another bin, a striking
dark-haired woman is taking a fresh one from a rack. She wears a jacket
emblazoned with the name "Desert Rose Nanomanufacturing."
"How'd you like it?" she asks with a smile.
"Pretty amazing," you say.
"Yes," she agrees. "I saw this sim back when I was taking my first
molecular-manufacturing class. I swore I'd never design anything so clunky! This
whole setup really brings back the memories—I can't wait to see if it's as crude
as I remember." She steps into the simulation hall and closes the door.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, or nanotech, is the
study and design of machines on the molecular and atomic level. To be
considered nanotechnology, these structures must be anywhere from 1 to
100 nanometers in size. A nanometer is equivalent to one-billionth of a
regular meter, which means that these structures are extremely small.
Researcher K. Eric Drexler was the first
person to popularize this technology in the early 1980’s. Drexler was
interested in building fully functioning robots, computers, and motors
that were smaller than a cell. He spent much of the 80’s defending his
ideas against critics that thought this technology would never be
possible.
Today, the word nanotechnology means
something a bit different. Instead of building microscopic motors and
computers, researchers are interested in building superior machines atom
by atom. Nanotech means that each atom of a machine is a functioning
structure on its own, but when combined with other structures, these
atoms work together to fulfill a larger purpose.
The U.S. National Nanotechnology
Initiative has large plans for nanotech. Mihail Roco, who is involved in
this organization, explains the group’s future plans by dividing their
goals into four generations.
The first generation of nanotech is
defined by passive structures that are created to carry out one specific
task. Researchers are currently in this generation of the
technology. The second generation will be defined by structures that can
multitask. Researchers are currently entering this generation and
hoping to further their abilities in the near future. The third
generation will introduce systems composed of thousands of
nanostructures. The last generation will be defined by Nano systems
designed on the molecular level. These systems will work like living
human or animal cells.
As nanotech continues to develop,
consumers will see it being used for several different purposes. This
technology may be used in energy production, medicine, and electronics,
as well as other commercial uses. Many believe that this technology will
also be used militarily. Nanotechnology will make it possible to build
more advanced weapons and surveillance devices. While these uses are not
yet possible, many researchers believe that it is only a matter of
time.
Uses of Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the study of the
manipulation of extremely small matter, including atoms and molecules.
Anything being developed or produced with the help of nanotechnology
usually has one dimension that is at least 1 to 100 nanometers in size.
To put it in perspective, if a meter was the Earth, a nanometer would be
a marble. At such a small stature, quantum mechanics becomes an
invaluable asset when observing the interactions between singular
molecules and/or atoms.
Nanotechnology can be applied during the
production of semiconductor chips, in which small molecules of matter
are laid out onto a tiny conductor chip, forming a vast matrix of
connections that is practically invisible to the human-eye. This
technology has laid the foundation for the Human race to be able to
produce new materials on the nano-scale, allowing for extreme
manipulation of even the most fleeting details within a molecule.
There is even investigation into whether
or not we will be able to directly control matter on a molecular or
atomic scale. This technology may sound like a god-send, but imagine a
scenario where the entire Earth is reduced to a pile of grey dust. The
culprit, a self-replicating nano-robot, is impossible to see or kill.
This Nano-robot would need energy to self-replicate, and would thus
search for the energy in its environment.
The result would be an exponential
explosion of Nano-bots with an unsatisfiable hunger for anything. The
arrival of this technology could either be a blessing or a plague, but
we get to choose which one we want.
Nanotechnology Products
Throughout history, much of the
technological progress made by humans has revolved around thinking big.
The Great Pyramids of Egypt, the Roman Coliseum, the Hoover Dam, all
have been on a grand scale. More recently, though, scientists and
engineers have been thinking smaller. From the transistors that replaced
vacuum tubes to give us radios that fit in the palm of one hand to the
microchips that shrunk computers from behemoths that once filled a room
to devices that fit in the palm of the other hand, the next big thing
now looks to be the next small thing – and that next small thing is
nanotechnology.
Nanotechnology is technology that deals with matter on the nano-scale,
between one and one hundred nanometers. (A nanometer is one billionth
of a meter.) Matter this tiny exists in a place where things work in a
different way than they do in the “normal” world. The seemingly bizarre
properties that matter displays on the nano-scale are precisely what
give nanotechnology products such intriguing potential.
With applications in many fields,
including medicine, solar energy, textiles, and manufacturing, many
nanotechnology products are already in use, with many more in advanced
stages of development. Among these nanotechnology products is NanoSphere,
a product developed by Schoeller Technologies that, when applied as a
coating to clothing, utilizes a self-cleaning property found in plant
leaves to allow dirt and residue to easily wash off with just a small
amount of water.
Other nanotechnology products include a
thin-film solar cell developed by Magnolia Solar which uses the quantum
properties of matter on the nano-scale to create solar cells that are
more efficient than those produced using conventional technology, thus
delivering on the promise of making solar energy affordable enough to
compete with fossil fuels.
Every day, scientists and engineers are
developing new nanotechnology products that have the potential to
revolutionize entire industries. Now more than ever, when it comes to
the cutting edge of technological advancement, it truly is a small
world.
Prakash Bacorisen
